By: Kelly O’Bannon | EVP, Business Development
Date: May 20th, 2025
Tracking mortgage delinquency trends is essential not just for lenders and servicers, but also for policymakers and homeowners navigating a market increasingly shaped by elevated costs and economic volatility. Although current delinquency rates remain below levels observed during historic crises such as the 2008 financial meltdown or the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, a convergence of persistent inflation, interest rate hikes, and escrow-related pressures is shifting the mortgage servicing landscape in meaningful ways. This blog aims to unpack the underlying causes of rising mortgage delinquencies, assess their implications for the servicing industry, and forecast industry responses amid a shifting economic landscape.
Historical Context: Lessons from Past Recessions
Mortgage delinquencies have historically been lagging indicators of economic distress. In past recessions—notably 1981–82 and 2007–09—delinquencies spiked due to unemployment, inflation, and home price crashes. The 2020 pandemic caused a sharp, short-lived spike mitigated by federal
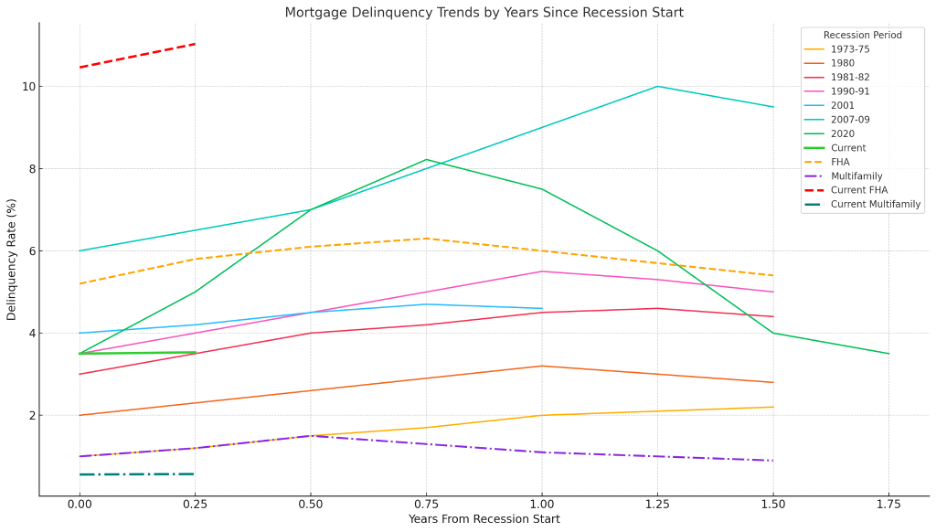
Today’s trends are different: Delinquencies are rising gradually, driven by sector-specific job losses and regional economic shifts rather than widespread unemployment. This nuanced pressure demands a more targeted servicing response.
The 2025 Mortgage Delinquency Landscape
As of Q4 2024, the national mortgage delinquency rate stood at 3.98%. This figure represents a modest increase from prior quarters but still falls well below the levels observed during previous economic downturns. However, beneath this seemingly stable surface lies a more complex narrative of divergent borrower experiences, with certain loan types and geographic regions experiencing outsized stress.
To illustrate these disparities, the following table provides a comparative look at delinquency rates by loan type:
| Loan Types | Delinquency Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| FHA Loans | 11.03% |
| VA Loans | 4.70% |
| Conventional Loans | 2.62% |
The delinquency rate for conventional loans has remained relatively low, largely due to stronger borrower credit profiles and widespread refinancing into low fixed rates during the 2020–2021 period. In contrast, government-backed loans, particularly those insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), have seen more significant challenges. FHA loans reported a delinquency rate of 11.03%, underscoring the greater vulnerability of first-time buyers and lower-income households who often lack the financial flexibility to absorb unexpected payment shocks. Loans backed by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) reported a mid-range delinquency rate of 4.70%, suggesting some moderate upward pressure.
Geographic disparities in delinquency rates also highlight the uneven distribution of risk. The chart below showcases the delinquency rates by state, revealing how location-based economic and environmental factors play a key role:
| State | Delinquency Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Louisiana | 8.6% |
| Mississippi | 8.3% |
| Alabama | 6.1% |
| Colorado | 2.1% |
| Washington | 2.0% |
| Idaho | 1.9% |
Gulf Coast and Southeastern states face disproportionate stress due to lower median incomes, climate risks, and rising insurance costs. Meanwhile, Western and Mountain states continue to see lower rates, typically hovering around 2%.
Key Drivers of Rising Delinquencies
Inflation and Mortgage Rates
The increase in delinquency rates can be attributed to a confluence of economic and structural factors that are applying pressure to household budgets. Chief among these are elevated interest rates, stubbornly high inflation, and increasing non-mortgage housing costs.
Since 2021, mortgage interest rates have more than doubled, with the national average for a 30-year fixed mortgage hovering near 6.9% as of early 2025. This surge has significantly increased borrowing costs, particularly for households that purchased homes or refinanced after 2021. For a typical mortgage of $300,000, the difference between a 3.1% and a 6.9% rate can translate to several hundred dollars more in monthly payments.
At the same time, inflation continues to chip away at real wages, making it more difficult for families to cover not only their mortgage obligations but also everyday expenses. Even as inflation moderates, the cumulative impact on household savings and purchasing power remains pronounced. The debt service ratio – representing the share of disposable income dedicated to debt repayments – has climbed to 11.3%, the highest level recorded since 2019.
Loan origination timing also plays a role. Borrowers who entered the market between 2022 and 2024 often did so at peak pricing, locking in higher rates and thinner equity positions. Many of these loans were underwritten with tighter margins, leaving borrowers especially exposed to payment shocks or income disruptions. FHA borrowers, in particular, remain at heightened risk due to lower credit thresholds and minimal down payment requirements.
Homeowners Insurance Premiums and Escrow Payment Increases
One of the most significant, yet often overlooked, contributors to the current wave of delinquencies is the rise in escrow payments, driven by escalating homeowners insurance premiums and property tax increases. While these costs are not part of a borrower’s base mortgage rate, they significantly affect the total monthly payment and often catch borrowers off guard.
Nationally, homeowners insurance premiums increased by 8.5% in 2024. However, in states like Florida, Texas, and California, rates rose by more than 25-30%, largely due to growing climate-related risks and insurer market withdrawals. At the same time, property taxes in high-growth metro areas have surged, fueled by rapid home price appreciation and local budget expansions.
| State | Avg. Insurance Premium Increase (%) |
|---|---|
| Florida | 32% |
| Texas | 28% |
| California | 26% |
| National Avg. | 8.5% |
As insurance premiums rise, so do escrow payments, which can significantly impact monthly mortgage payments. For many borrowers, escalating property taxes may drive unexpected payment shocks. Escrow increases strain budgets and elevate delinquency risks.
Leading Economic Indicators and Mortgage Delinquency Trends
Understanding the forward-looking signals that can foreshadow mortgage delinquency shifts is critical for lenders and policymakers alike. The interplay between employment trends, debt burdens, and home price movements provides a predictive framework for assessing where risks may intensify next.
- Labor Market Conditions: As of March 2025, the national unemployment rate remains relatively low at 4.2%, with weekly initial jobless claims hovering around 220,000. These figures suggest that most borrowers currently retain the income necessary to stay current on their mortgages. However, this picture can change quickly. In prior recessions, surges in unemployment claims were often followed by rising delinquencies just a few months later. If jobless claims were to climb steadily over several consecutive weeks, it would be an early signal of looming distress in the mortgage market.
- Debt Burdens: The household debt service ratio (DSR) climbed to 11.3% in the fourth quarter of 2024, marking the highest level recorded since 2019. Rising DSR levels show that a larger portion of disposable income is being absorbed by debt repayments, which reduces borrowers’ financial flexibility to manage unexpected costs or economic shocks. Higher revolving debt balances, such as credit card debt, combined with elevated mortgage payments, are eroding the financial cushion many households rely upon. This environment increases the likelihood of missed mortgage payments, particularly among first-time buyers and moderate-income households
- Home Prices: While national home prices have largely stabilized, regional disparities are emerging. In certain metropolitan areas like Cape Coral, FL, and Austin, TX, home prices have started to decline year-over-year. Shrinking equity buffers heighten the risk of negative equity situations, where borrowers owe more than their homes are worth. Historically, borrowers with negative or minimal equity are more likely to default, especially if they encounter income loss or rising living expenses. Monitoring market-specific trends is essential for early detection of localized delinquency risk.
Altogether, these indicators suggest a cautious outlook. While no immediate national crisis is forecasted, a gradual uptick in delinquencies appears likely in certain pockets.
Industry Outlook and Responses
While current delinquency rates remain moderate by historical standards, short-term risk remains elevated. Continued inflationary pressure, high interest rates, and the growing burden of escrow-related costs, especially in states experiencing insurance market disruption are likely to drive further increases in delinquency rates into the near future.
In this changing environment, servicers must carefully balance operational accuracy with a compassionate approach toward borrowers. Organizations that align forward-looking strategic planning with operational agility, and those that leverage technology not solely for cost reductions but also to improve the borrower experience, will be best equipped to transform today’s challenges into long-term strengths.
Staying Ahead Together
The mortgage servicing landscape of 2025 is characterized by complexity and regional variability, yet remains manageable with a proactive approach. Although a systemic crisis akin to 2008 appears unlikely, localized stress among specific borrower groups requires heightened attention.
Servicers who focus on blending operational efficiency with borrower-centric strategies will be best positioned to succeed. Prioritizing investments in predictive analytics, enhancing regional outreach initiatives, and refining borrower communication practices are critical steps for navigating the challenges ahead.
At Midwest Loan Services, we remain committed to partnering with our clients to protect and sustain homeownership. By integrating cutting-edge technology with a human-centered servicing philosophy, we aim to foster greater stability for borrowers, regardless of market conditions.
Contact us today to learn how Midwest Loan Services can support your servicing strategy or borrower engagement efforts. Together, we can make homeownership stable, sustainable, and secure.








